What is the FDIC?
The FDIC is short for the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation, an independent US government agency. The FDIC protects depositors of insured banks in the United States against losing their deposits if an insured bank fails. Any person or entity can have FDIC insurance coverage in an insured bank.
What does the FDIC cover?
- Checking accounts
- Negotiable Order of Withdrawal (NOW) accounts
- Savings accounts
- Money Market Deposit Accounts
- Time deposits such as Certificates of Deposits (CDs)
- Cashier's checks, money orders, and other official terms issued by a bank.
What does the FDIC not cover?
- Stock investments
- Bond investments
- Mutual funds
- Life insurance policies
- Annuities
- Municipal securities
- Safe deposit boxes or their contents
- U.S. Treasury bills, bonds, or notes
Coverage Limits
The standard deposit insurance amount is $250,000 per depositor, per insured bank, for each account ownership category. So, what are the ownership categories?
Single Accounts: The FDIC adds all single accounts owned by the same person at the same bank and insures up to $250,000.
Certain Retirement Accounts (IRAs, self-directed defined contribution plan accounts, self-directed Keogh plan account, section 457 deferred compensation plan account): The FDIC adds all retirement accounts owned by the same person at the same bank and insures up to $250,000.
Joint Accounts: Each co-owner's shares of every joint account that he or she owns at the same insured bank are added together, and the total is insured up to $250,000. All co-owners must be living people with equal rights to withdraw deposits from the account. All co-owners must have personally signed to show proof of co-ownership.
Revocable Trust Accounts: When a revocable trust owner names five or fewer beneficiaries, the owner's trust deposits are insured up to $250,000 for each beneficiary.
Irrevocable Trust Accounts: The interests of a beneficiary in all deposit accounts under an irrevocable trust established by the same settlor and held at the same insured bank are added together and insured up to $250,000. The trust must be valid under state law, the insured bank's deposit account records must disclose the existence and conditions of the trust relationship, and the amount of each beneficiary's interest must not be contingent as defined by FDIC regulations.
Employee Benefit Plan Accounts: The FDIC insures up to $250,000 for the noncontingent interest of each plan participant.
Corporation/Partnership/Unincorporated Association Accounts: All deposits owned by a corporation, partnership, or unincorporated association at the same bank are combined and insured up to $250,000.
Government Accounts (also called Public Unit accounts): The FDIC insures up to $250,000 per official custodian (more coverage available subject to specific conditions).
Example FDIC Coverage:
Insurance coverage for a Husband and Wife with Deposit Accounts in Multiple Ownership Categories
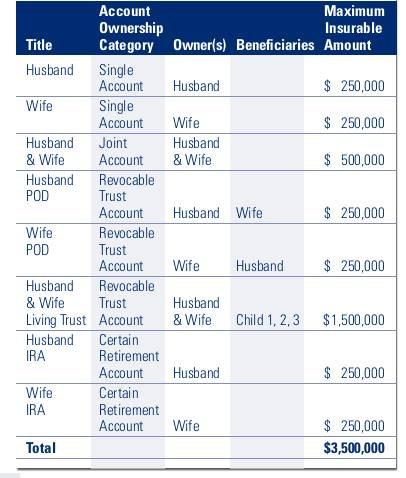
Source: https://www.fdic.gov/resources/deposit-insurance/understanding-deposit-insurance/